Ecological Archives E096-116-A1
Sara Tomiolo, Wim H. van der Putten, and Katja Tielbörger. 2015. Separating the role of biotic interactions and climate in determining adaptive response of plants to climate change. Ecology 96:1298–1308. http://dx.doi.org/10.1890/14-1445.1
Appendix A. Detailed description of the study sites and of the experimental set up.
Table A1. Description of the sites' characteristics and position along the gradient. Meteorological data provided by the Israel Meteorological Service (http://www.ims.gov.il/IMSEng/CLIMATE); mean rainfall and coefficient variation (CV) were calculated using long term records stretching over an interval of 55 years (1950-2005) in each sowing site. Note that the results from the Arid site were discarded because of almost complete mortality of the sown plants.
Study Sites |
Coordinates |
Altitude |
Mean T (°C) |
Soil classification |
Mean annual rainfall |
Rainfall recorded |
Vegetation |
Mediterranean (M) |
31°42'N |
620 |
17.7 |
Terra Rossa |
550; 31 |
356 |
Dwarf Shrubland, annuals |
semi-arid |
31°23N |
590 |
18.4 |
Brown Rendzina |
270; 38 |
177 |
Dwarf Shrubland, annuals |
arid (A) |
30°52'N |
470 |
19.1 |
Deseert lithosol |
90; 51 |
<50 |
Sparse shrubs, annuals |
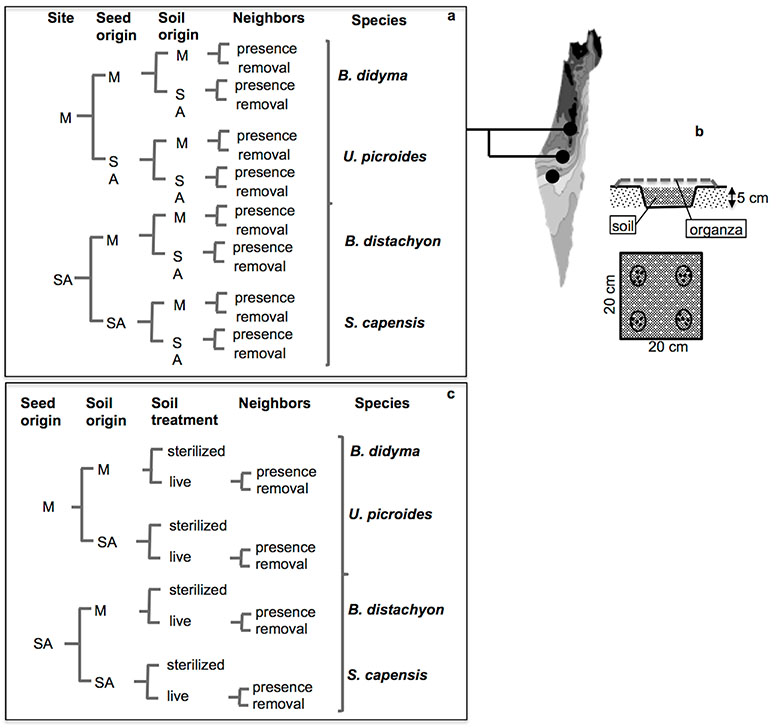
Fig. A1. Organization of experimental set-up. (a) Field experimental set up: in the field site (i.e., rainfall), seed origin, soil origin and neighbor treatments were combined in a full factorial fashion, resulting in 8 treatments that were replicated 10 times at each site (represented on the map on the side). (b) Schematic representation of a plot in the field. Each plot was 5 cm deep, filled with soil and covered with a layer of organza until germination in order to prevent secondary contamination. Each plot was a quadrat of 20 × 20 cm and the four target species were sown at each corner within 5 cm wide plastic rings that were removed after germination. (c) Experimental set-up in the greenhouse: seed origin, soil origin, soil treatment and neighbor treatment were combined in a full factorial design. Because sterilization killed the seed bank in the soil, it was not possible to have a treatment combining presence of neighbors and sterilized soil. The combination of all factors determined 12 treatments that were replicated 12 times.