Ecological Archives E096-028-A1
Alison B. Duncan, Andrew Gonzalez, and Oliver Kaltz. 2015. Dispersal, environmental forcing, and parasites combine to affect metapopulation synchrony and stability. Ecology 96:284–290. http://dx.doi.org/10.1890/14-0137.1
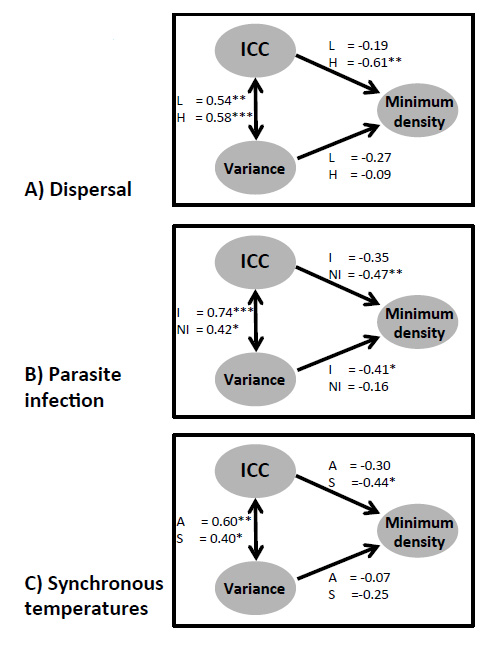
Appendix A. A figure showing the direct and indirect effects of the intraclass correlation coefficient and metapopulation variance on minimum metapopulation size.
Figures show path correlation coefficients divided for: A) Dispersal (H = high, L = low), B) parasite infection (I = infected, NI = non infected) and C) synchronous temperatures (A = asynchrony, S = synchrony). |
 |
Fig. A1. The direct and indirect effects of the intraclass correlation coefficient and metapopulation variance on minimum metapopulation size. Numbers denote path correlation coefficients calculated using standardised beta regression coefficients. (note * = p < 0.05, ** p < 0.001 and *** = p < 0.0001).