Ecological Archives E096-016-A2
Kristin L. Matulich and Jennifer B. H. Martiny. 2015. Microbial composition alters the response of litter decomposition to environmental change. Ecology 96:154–163. http://dx.doi.org/10.1890/14-0357.1
Appendix B. Supplementary results: microbial composition affects a model ecosystem’s functional response to environmental change.
Table B1. Bacterial and fungal composition of the 8 community assemblages (grouped by taxonomic phylum and family), whether the strain was detected in pyrosequencing of the inoculated microcosm litter, and it's corresponding GenBank accession number. If the strain was detected in natural litter pyrosequencing data, its percent abundance in these libraries ("Natural Abundance") is also shown. Some strains that were identified in the microcosm pyrosequencing data but were not or rarely detected in a natural leaf litter community are identified as (-) and (negligible), respectively. Lastly, the natural abundance of taxonomic families is shown.
Bacterial Strains |
Community |
Detected in Sequencing Data |
Accession Number |
Natural Abundance (%) |
Natural Abundance of Family (%) |
|||||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|||||||
Actinobacteria |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Cellulomonadaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.001 |
|
|
|
Cellulomonas sp. |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
KF881975 |
|
|
|
Microbacteriaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37.400 |
|
|
|
Clavibacter michiganensis |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
KF733313 |
|
|
|
|
Cryocola sp. |
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
|
KF733303 |
|
|
|
|
Curtobacterium sp. |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733300 |
18.638 |
|
|
|
Frigoribacterium sp. |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
KF881977 |
|
|
|
|
Microbacteriaceae sp. 1 |
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF881980 |
- |
|
|
|
Microbacteriaceae sp. 2 |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
KF881976 |
|
|
|
|
Microbacteriaceae sp. 3 |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF881981 |
- |
|
|
|
Microbacterium sp. |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
KF881979 |
|
|
|
|
Plantibacter cousiniae |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF733314 |
0.227 |
|
|
|
Schumannella luteola |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733311 |
negligible |
|
|
|
Schumannella sp. |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
KF881974 |
|
|
|
Micrococcaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.463 |
|
|
Arthrobacter sp. |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733309 |
0.122 |
|
|
Nocardiaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.449 |
|
|
Nocardiaceae sp. |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733304 |
0.956 |
|
|
|
Rhodococcus cercidiphylli |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF733316 |
0.162 |
|
|
|
Rhodococcus sp. |
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733317 |
0.162 |
|
|
Sanguibacteraceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.265 |
|
|
Sanguibacter sp. 1 |
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733318 |
0.287 |
|
|
|
Sanguibacter sp. 2 |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
KF733319 |
|
|
Bacteriodetes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Flexibacteraceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.575 |
|
|
Dyadobacter sp. |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF733324 |
0.214 |
|
|
Flavobacteriaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.054 |
|
|
Flavobacterium sp. |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF733322 |
0.275 |
|
|
Sphingobacteriaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.052 |
|
|
Pedobacter borealis |
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733323 |
0.008 |
|
Proteobacteria |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Hyphomicrobiaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.607 |
|
|
Devosia sp. |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF881983 |
0.378 |
|
|
Oxalobacteraceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.506 |
|
|
Duganella zoogloeoides |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733339 |
0.151 |
|
|
Pseudomonadaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.008 |
|
|
Pseudomonas fluorescens |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733338 |
0.003 |
|
|
|
Pseudomonas sp. 1 |
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
KF733326 |
|
|
|
|
Pseudomonas sp. 2 |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733336 |
- |
|
|
|
Pseudomonas sp. 3 |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733329 |
0.003 |
|
|
|
Pseudomonas synxantha |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733328 |
0.003 |
|
|
Rhizobiaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.578 |
|
|
Rhizobium sp. |
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF881978 |
negligible |
|
|
Sphingomonadaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.537 |
|
|
Novosphingobium sp. |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF881984 |
0.425 |
|
|
|
Sphingomonas sp. |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
KF881985 |
|
|
|
Not Classified |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Erythrobacteraceae sp. |
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF881982 |
0.203 |
|
|
||||||||||||||
Fungal Strains |
Community |
Detected in Sequencing Data |
Accession Number |
Natural Abundance (%) |
Natural Abundance of Family (%) |
|||||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|||||||
Ascomycota |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Sphingomonadaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.191 |
|
|
Neofusicoccium sp. |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733350 |
- |
|
|
Diatrypaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
negligible |
|
|
Phaeomoniella sp. |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF733354 |
negligible |
|
|
Dothideaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.634 |
|
|
Dothidea sp. |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733353 |
- |
|
|
Hypocreaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
negligible |
|
|
Hypocreales koningii |
|
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733347 |
- |
|
|
|
Hypocreales sp. |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733366 |
negligible |
|
|
Lasiosphaeriaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.451 |
|
|
Cercophora sp. 1 |
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733357 |
|
|
|
|
Cercophora sp. 2 |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF881973 |
|
|
|
Nectriaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.102 |
|
|
Gibberella sp. |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733374 |
0.029 |
|
|
Pleosporaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.829 |
|
|
Alternaria sp. 1 |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF733341 |
- |
|
|
|
Alternaria sp. 2 |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF733365 |
- |
|
|
|
Lewia sp. |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733349 |
- |
|
|
Phaeosphaeriaceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.770 |
|
|
Pleosporales sp. 1 |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733356 |
0.032 |
|
|
|
Pleosporales sp. 2 |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
X |
KF733370 |
0.032 |
|
|
Not Classified |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Camarosporium brabeji |
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733369 |
negligible |
|
|
|
Dothideomycetes sp. |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733351 |
- |
|
|
|
Helotiales sp. 1 |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
X |
KF733352 |
- |
|
|
|
Helotiales sp. 2 |
|
X |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733364 |
- |
|
|
|
Sordariomycetes sp. |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733373 |
negligible |
|
Basidiomycota |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Not Classified |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cryptococcus sp. 1 |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
KF733355 |
|
|
|
|
Cryptococcus sp. 2 |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
X |
KF733358 |
0.669 |
|
|
|
Cryptococcus sp. 3 |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
KF733368 |
|
|
|
|
Cryptococcus sp. 4 |
|
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
KF733375 |
|
|
Zygomycota |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Mucoraceae |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
negligible |
|
|
Mucor racemosus 1 |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733344 |
negligible |
|
|
|
Mucor racemosus 2 |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
KF733345 |
negligible |
|
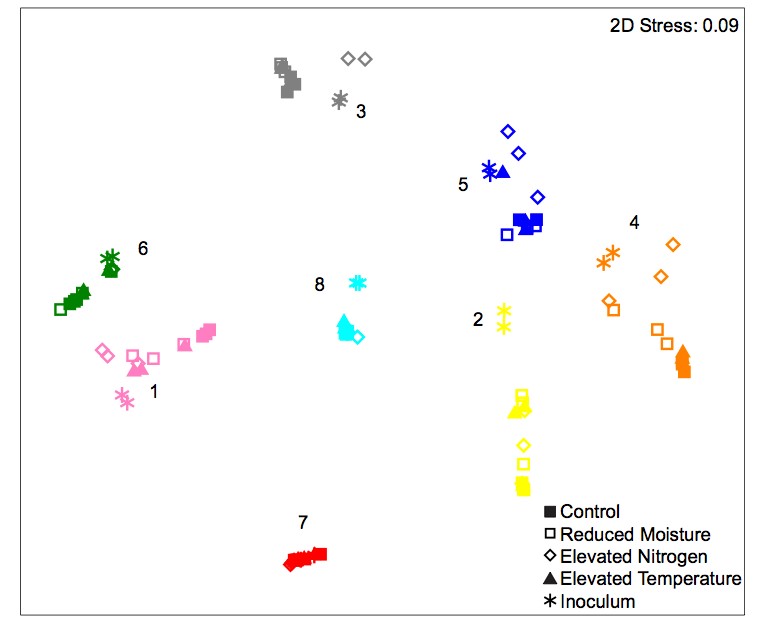
Fig. B1. Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination based on Bray Curtis similarites depicting bacterial community composition. The samples inoculated with the same initial microbial community are displayed in the same symbol color (8 communities total). The shape of the symbols represent the environmental treatment, either control conditions (filled squares), reduced moisture (open squares), elevated nitrogen (diamonds), and increased temperature (triangles). The initial microbial inoculum (stars) is also plotted and identified by community assemblage but excluded from analyses. N = 3 per community and treatment combination.
Fig. B2. Total community richness (bacterial and fungi) for each treatment by the eight microbial communities. Gray boxes represent initial community richness of inoculum, blue boxes represent microcosms in control conditions, yellow in reduced moisture, green in elevated nitrogen, and red in elevated temperature. N = 3 for each box. Asterisks (*) represent significant difference between treatment and control conditions, and crosses (+) represent significant difference between inoculum and treatment. Significant variations determined from Tukey post hoc test.
Fig. B3. Daily microbial respiration rates of each sampling period averaged over all microbial communities for each environmental treatment. Blue points represent microcosms in control conditions, yellow in reduced moisture, green in elevated nitrogen, and red in elevated temperature. N = 48 for each point.