Ecological Archives A017-046-A8
Martin Hoyle and James E. Creswell. 2007. The effect of wind direction on cross-pollination in wind-pollinated GM crops. Ecological Applications 17:1234–1243.
Appendix H. Wind direction simulation.
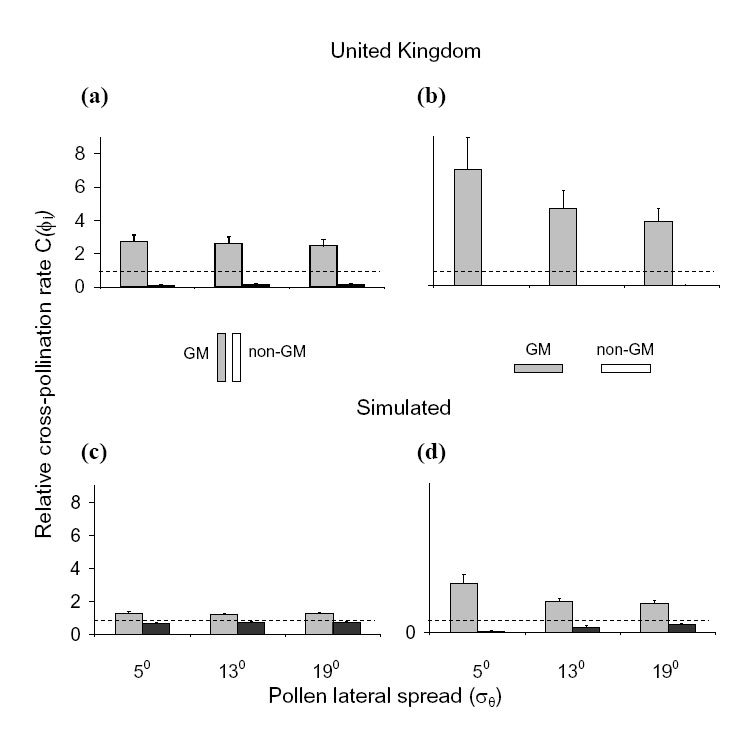
As mentioned in the main text, by simulating random wind directions for each hour, we estimated the variability in cross-pollination rates due only to sampling a finite number of hourly observations. A large component of the variability found in real data is due to the non-random variation in wind direction (Fig. H1).
|
| |
FIG. H1. Average maximum (maxi[C(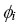 )]) (gray shading) and minimum (mini[C( )]) (gray shading) and minimum (mini[C(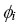 )]) (dark shading) relative cross-pollination rates across field orientations ( )]) (dark shading) relative cross-pollination rates across field orientations (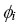 ) for maize, as a function of the lateral spread of pollen ( ) for maize, as a function of the lateral spread of pollen (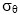 ), geometry of the fields, and pattern of wind direction. The wind directions in (a) and (b) are the UK average, and in (c) and (d) simulated random directions for each hour. There is no allowance for wind speed in pollen release. Error bars represent ± 1 standard deviation.
Meani{C( ), geometry of the fields, and pattern of wind direction. The wind directions in (a) and (b) are the UK average, and in (c) and (d) simulated random directions for each hour. There is no allowance for wind speed in pollen release. Error bars represent ± 1 standard deviation.
Meani{C(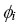 )} = 1 (dotted lines) independently for each field geometry. )} = 1 (dotted lines) independently for each field geometry. |
[Back to A017-046]

